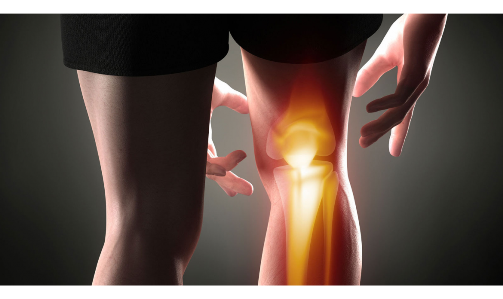
ARTHRITIS OVERVIEW
Arthritis, a term that covers different joint problems, shows up as swelling, ache, and rigidity. This widespread ailment affects many people around the world, demanding a proper treatment for long lasting relief from joint pain.
SYMPTOMS OF ARTHRITIS
The symptoms of arthritis are diverse, ranging from joint pain and swelling to stiffness and reduced range of motion. The manifestation can vary in intensity, significantly affecting an individual’s quality of life.
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary not only between different types of arthritis but also among individuals with the same type of arthritis. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective management, so if someone is experiencing persistent joint symptoms, they should seek medical evaluation and advice.
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the specific type of arthritis a person has. However, there are common symptoms that may be indicative of arthritis:
Joint Pain: Persistent pain in one or more joints is a hallmark symptom of arthritis. The pain may be dull or sharp and can range from mild to severe.
Joint Stiffness: Arthritis often causes stiffness in the affected joints, especially after periods of inactivity. Morning stiffness is a common complaint among individuals with arthritis.
Swelling: Inflamed joints may appear swollen and feel warm to the touch. This swelling is caused by an accumulation of excess fluid in the joint.
Redness and Warmth: The skin over the affected joint may become red and warm due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
Reduced Range of Motion: Arthritis can lead to a decreased range of motion in the affected joints. Individuals may find it challenging to move their joints fully.
Fatigue: Many people with arthritis experience fatigue, which can be attributed to the body’s response to chronic inflammation and the effort required to cope with pain and stiffness.
Weakness and Muscle Atrophy: Over time, the muscles around the affected joints may weaken, and there can be a loss of muscle mass (atrophy).
Joint Deformities: In some types of arthritis, prolonged inflammation can lead to joint deformities. For example, fingers may take on a twisted appearance.
Tenderness: The affected joints may be tender to the touch, and even light pressure can cause pain.
Fever and Weight Loss: In certain inflammatory forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, individuals may experience systemic symptoms like fever and unintentional weight loss.
CAUSES OF ARTHRITIS
Understanding the specific cause of arthritis is crucial for determining the most effective treatment and management strategies. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan based on the type of arthritis and its underlying causes. There are several causes of arthritis, and the specific factors can vary depending on the type of arthritis. Here are some common causes:
Age: Osteoarthritis, the most prevalent form of arthritis, is often associated with aging. The wear and tear on joints over time can lead to the breakdown of cartilage, causing pain and stiffness.
Genetics: Some forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, may have a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of arthritis may be more predisposed to developing the condition.
Autoimmune Disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium (the lining of the membranes that surround the joints). This immune response causes inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
Infections: Infections caused by bacteria or viruses can lead to certain types of arthritis. Reactive arthritis, for example, may occur after an infection in another part of the body.
Injury and Trauma: Joint injuries or trauma, such as fractures or dislocations, can increase the risk of developing arthritis. Post-traumatic arthritis may develop in a joint that has been injured in the past.
Metabolic Abnormalities: Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joints. This condition is often associated with metabolic abnormalities and is influenced by dietary factors.
Lifestyle Factors: Obesity is a risk factor for osteoarthritis, particularly in weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips. Excess body weight puts additional stress on joints, accelerating the wear and tear process.
Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, may contribute to the development of certain types of arthritis. For example, the risk of rheumatoid arthritis may be influenced by hormonal fluctuations.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational hazards, may increase the risk of developing certain types of arthritis.
Other Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions, such as lupus or psoriasis, can contribute to the development of arthritis. These conditions involve the immune system and can affect joint health.
PREVENTION OF ARTHRITIS
Preventing arthritis involves adopting a holistic approach that addresses various lifestyle factors. Here are some preventive measures to reduce the risk of developing arthritis:
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate-intensity exercise to strengthen muscles and maintain joint flexibility. Include activities that promote cardiovascular health, strength training, and flexibility, contributing to overall joint health.
Proper Warm-Up and Stretching: Always warm up before engaging in physical activity to prepare muscles and joints. Incorporate stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries, fostering joint resilience.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Manage body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce stress on joints, particularly in weight-bearing areas like the knees and hips. Weight management is crucial in preventing arthritis and alleviating strain on joints.
Ergonomic Practices: Maintain proper body mechanics and posture during daily activities. Use ergonomic furniture and tools to reduce strain on muscles and joints, minimizing the risk of joint-related issues.
Stay Hydrated: Ensure adequate hydration to support joint lubrication and overall musculoskeletal health. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining the health and functionality of joints.
Balanced Diet: Consume a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients, including calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids to support bone and joint health. A nutritious diet plays a vital role in preventing arthritis and promoting overall musculoskeletal well-being.
Protective Gear: When engaging in activities that pose a risk of injury, use appropriate protective gear such as knee pads, helmets, or supportive footwear. Protective gear can help prevent injuries that may contribute to arthritis development.
Avoid Overexertion: Pace yourself during physical activities to prevent overuse injuries. Take breaks and listen to your body’s signals, preventing excessive strain on joints that could lead to arthritis over time.
Proper Footwear: Wear supportive and comfortable shoes that provide adequate arch support. Replace worn-out shoes to maintain proper foot alignment, reducing the impact on joints, especially those in the lower extremities.
Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule regular health check-ups to monitor overall health and address any emerging concerns promptly. Early detection and management of health issues contribute to preventing arthritis complications.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and exacerbate joint pain, making stress management an essential aspect of arthritis prevention.
Avoid Smoking: Quit smoking, as it can negatively impact blood circulation and overall tissue health. Smoking cessation contributes to better vascular health, reducing the risk of arthritis-related complications.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption may contribute to inflammation and joint problems. Moderation in alcohol consumption supports overall joint health.
Bone Health: Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake to support bone health. Consider supplements if needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, promoting skeletal strength and reducing the risk of arthritis.
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to early signs of discomfort or pain, and take appropriate measures to address them promptly. Listening to your body’s signals is crucial in preventing the progression of potential joint issues into arthritis.
DIAGNOSIS FOR ARTHRITIS
Accurate diagnosis of arthritis involves a meticulous examination of medical history, physical assessments, and imaging tests. Early detection of signs and symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and improved outcomes of arthritis treatment. Diagnosing arthritis involves a meticulous evaluation by healthcare professionals to uncover the underlying causes contributing to joint and muscular pain. Here are key aspects of the diagnostic process tailored to arthritis:
Medical History: A comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history is conducted, encompassing previous injuries, chronic conditions, and a thorough examination of family history, particularly focusing on musculoskeletal disorders.
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is performed to assess joint function, muscle strength, range of motion, and the presence of signs indicating inflammation or deformity, all of which are crucial in arthritis diagnosis.
Symptom Assessment: In-depth discussions about the nature and location of pain, its onset, duration, and factors that alleviate or exacerbate symptoms provide valuable insights into the specific characteristics of arthritis-related discomfort.
Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: Utilized to visualize bones, detect fractures, arthritis, or structural abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, ligaments, and tendons, aiding in the identification of arthritis-related changes.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Useful for detailed imaging of bones and joints, particularly beneficial in assessing structural aspects of arthritis.
Blood Tests: Blood tests play a crucial role in assessing inflammatory markers, detecting autoimmune conditions, and identifying markers of infection that may contribute to arthritis.
Joint Aspiration: The removal of a small sample of fluid from the affected joint allows for analysis, aiding in the identification of signs of infection, inflammation, or crystal deposits, contributing to arthritis diagnosis.
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: Electrophysiological tests are employed to assess nerve function and identify issues related to the peripheral nervous system, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of arthritis-related symptoms.
Bone Scans: Nuclear medicine imaging is employed to detect bone abnormalities, such as fractures or bone infections, offering additional insights into arthritis-related complications.
Ultrasound: Real-time imaging using sound waves assesses soft tissues, joints, and helps detect inflammation or fluid accumulation, aiding in arthritis diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation by Specialists: Consultation with specialists, including rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons, or neurologists, is sought based on the suspected underlying causes of arthritis, ensuring a targeted and specialized approach.
Diagnostic Injections: Local anesthetic or anti-inflammatory injections into joints or trigger points aid in assessing pain relief, assisting in pinpointing the specific source of arthritis-related discomfort.
Medical Imaging Interpretation: Radiologists interpret imaging studies to identify abnormalities and correlate findings with clinical symptoms, contributing to the accuracy of arthritis diagnosis.
Rule Out Differential Diagnoses: Considering and ruling out other conditions that may mimic arthritis symptoms, such as vascular issues or referred pain from internal organs, ensures a precise and focused approach to arthritis diagnosis.
ALLOPATHY APPROACH IN MANAGING ARTHRITIS
In the realm of modern-day medicinal drug, arthritis is addressed through a variety of treatments, along with analgesics, anti-inflammatory tablets, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These interventions intend to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the ailment.
Benefits
Quick Relief: Modern medication presents quick comfort from ache and irritation.
Advanced Interventions: For severe instances, superior medical interventions are to be had to manipulate arthritis effectively.
Shortfalls
Potential Side Effects: Medications can also come with facet results that want to be carefully managed.
Symptom Management: The cognizance frequently leans towards handling signs rather than addressing the underlying causes.
AYURVEDA APPROACH IN MANAGING ARTHRITIS
Ayurveda, an historic Indian gadget of drugs, gives holistic techniques to arthritis management via herbal remedies and life-style adjustments.
Benefits
Natural Remedies: Ayurveda emphasizes herbal remedies with minimal aspect effects.
Holistic Approach: Ayurvedic practices take into account ordinary properly-being, addressing the root causes of arthritis.
Shortfalls
Gradual Results: Ayurvedic procedures may additionally yield gradual outcomes, requiring endurance and commitment.
ROLE OF PANCHKARMA IN ARTHRITIS MANAGEMENT
Panchkarma, a quintessential component of Ayurveda, involves cleansing and rejuvenating therapies. It plays a pivotal role in addressing the root causes of arthritis and promoting overall well-being. Some of the effective Panchkarma Therapies that can provide long-lasting relief from Arthritis are: Abhyangam, Swedanam, Potli Mardan (massage), etc. In essence, Panchkarma in managing arthritis operates on a holistic principle, addressing the physical, mental, and emotional aspects of an individual. This comprehensive approach not only alleviates symptoms but also focuses on preventing the recurrence of arthritis, promoting long-term joint health and overall wellness.
Panchkarma, an integral component of Ayurveda, plays a significant role in the comprehensive management of arthritis. This holistic approach focuses on restoring balance to the body, eliminating toxins, and promoting overall well-being. Here’s an exploration of the key roles of Panchkarma in managing arthritis:
Detoxification (Shodhana): Detoxification through Panchkarma helps clear channels and remove toxic substances, reducing inflammation and addressing the root causes of arthritis.
Vamana (Therapeutic Emesis): Administering controlled vomiting to eliminate excess Kapha (one of the doshas) and toxins.
Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Inducing controlled bowel movements to remove accumulated Pitta and toxins from the body.
Balancing Doshas: Balancing the doshas, particularly Vata, is crucial in managing arthritis as an imbalance is often associated with joint pain and inflammation.
Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Therapeutic massage using herbal oils to balance Vata and improve joint flexibility.
Swedana (Steam Therapy): Inducing sweating through steam to balance Vata and reduce stiffness.
Joint-Specific Therapies: Joint-specific Panchkarma therapies provide targeted relief to affected areas, reducing inflammation and promoting joint health.
Basti (Enema Therapy): Administering medicated enemas to address Vata imbalances and nourish joints.
Janu Basti (Knee Basti): Focusing on the knee joints to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Strengthening and Rejuvenation: Strengthening and rejuvenating therapies contribute to enhanced joint resilience and improved overall health, vital in managing arthritis.
Rasayana Therapy: Administration of rejuvenating formulations to strengthen tissues and improve overall vitality.
Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): Purifying the blood to remove impurities and toxins.
Lifestyle Modification Guidance: Panchkarma extends beyond therapies, offering guidance on lifestyle modifications crucial for sustaining the benefits of the treatment and preventing arthritis recurrence.
Dietary Recommendations: Providing personalized dietary guidelines, emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods and herbs.
Yoga and Meditation: Recommending specific yoga postures and meditation techniques to manage stress and enhance joint flexibility.
Patient-Specific Approaches: Tailoring Panchkarma approaches to the specific needs and conditions of each patient ensures a personalized and effective treatment plan.
Nasya (Nasal Administration): Administering medicated oils through the nasal passages for conditions affecting the head and neck.
Kavala Graha (Oil Pulling): Swishing medicated oils in the mouth for oral health, which is linked to overall well-being.
Psychological Well-being: Addressing psychological aspects is integral in managing arthritis, and therapies like Shirodhara contribute to stress reduction and mental well-being.
Shirodhara (Oil Pouring on Forehead): Pouring warm oil on the forehead to induce relaxation and balance the nervous system.
ARTHRITIS TREATMENT AT DR MONGA MEDI CLINIC
Arthritis, a prevalent joint disorder, can be a challenging condition to manage. At Dr. Monga Clinic, we offer a holistic approach to arthritis treatment, incorporating traditional Ayurvedic practices, with a special focus on Panchkarma therapies.
What sets our approach apart is the personalized touch. Our Ayurvedic experts assess individual constitutions and arthritis types, ensuring tailored Panchkarma therapies for optimal results. The integration of ancient practices with modern medicine provides a balanced and effective treatment plan, offering relief and revitalization to those grappling with arthritis.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
While complete cure may not always be attainable, effective management significantly improves the quality of life.
Absolutely. Ayurveda offers a plethora of natural remedies, including herbal formulations and dietary recommendations.
Panchkarma is tailored to individual needs. Consultation with our experts helps determine its suitability for each patient.