THYROID DISORDER OVERVIEW
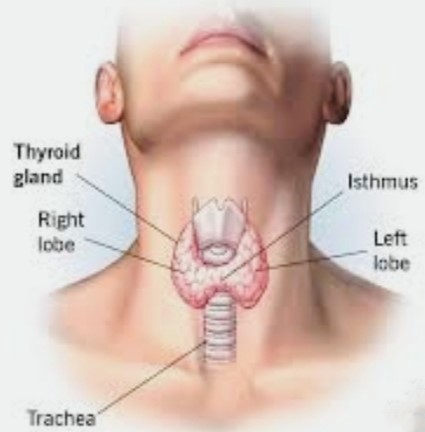
Thyroid disease refers to a group of medical conditions that affect the normal function of the thyroid gland, which is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that plays an important role in regulating body functions by producing thyroid hormones, a helps to raise metabolism, . growth and development
There are several types of thyroid disease:
Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold tolerance, dizziness, dry skin and nausea. Hypothyroidism Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease, can be caused by thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, certain medications, or congenital factors.
Hyperthyroidism: Unlike hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland that produces too much thyroid hormone Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, increased appetite , shaking, sweating and heat intolerance. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease.
Thyroid nodules: Thyroid nodules are small lumps or growths that can form in the thyroid gland. They are usually non-cancerous (not cancerous), but in some cases they can be cancerous. Thyroid nodules usually do not cause obvious symptoms, but they can be diagnosed during physical examination or by imaging studies. Further investigations are needed to diagnose the tissue and guide appropriate treatment.
Thyroid Cancer: Thyroid cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the thyroid gland grow and develop out of control. Appears as lumps or ulcers in the throat. Most thyroid cancers have a good prognosis, with a high survival rate if detected and treated early.
Treatment options include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, external radiation, or targeted therapy. It usually involves a review of medical history, a physical examination, blood tests to measure hormone levels, imaging tests (such as an ultrasound or thyroid scan), and sometimes a needle aspiration of the fine-needle examination for thyroid disease and suggests a suspicious thyroid nodule. and combined with Treatment for hypothyroidism depends on the specific condition and the underlying cause.
Options may include medication (such as synthetic thyroid hormone or antithyroid drugs), iodine therapy with radioactive iodine, surgery (partial or total thyroidectomy), or in some cases , cautious waiting for benign tissue is needed to continue monitoring thyroid dysfunction and ensuring optimal hormone levels and overall health m is maintained.
Consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as an endocrinologist, for an accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment and personal care for thyroid disease.
SYMPTOMS OF THYROID DISORDERS
Thyroid disease can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on whether it is hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (overactive thyroid) Here are some common symptoms associated with thyroid disease.
- Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Cold intolerance (feeling cold when others are comfortable)
- Dry skin and hair
- Brittle nails
- Constipation
- Depression and mood changes
- Muscle weakness or aches
- Memory problems and difficulty concentrating
- Menstrual irregularities or heavy periods in women
- Slowed heart rate
- Swelling of the face, hands, or feet
- Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
- Unexplained weight loss, despite increased appetite
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Feeling anxious, irritable, or restless
- Tremors or shaking hands
- Increased sweating and heat intolerance
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Fatigue or muscle weakness
- Frequent bowel movements or diarrhea
- Lighter or irregular menstrual periods in women
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), causing a visible swelling in the neck
- Eye problems (in Graves’ disease), such as bulging eyes, double vision, or eye irritation
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and may not be unique to thyroid disease. If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect thyroid problems, it’s best to talk to a healthcare professional for proper testing, diagnosis and treatment
CAUSES OF THYROID DISORDERS
Thyroid disorders can have various causes, depending on the specific condition. Here are some common causes associated with thyroid disorders:
- Hypothyroidism Causes:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: This is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and gradual destruction of thyroid tissue.
- Iodine deficiency: Inadequate intake of iodine, an essential nutrient required for the production of thyroid hormones, can contribute to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid surgery or radiation therapy: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland or radiation treatment for conditions like thyroid cancer can result in reduced thyroid hormone production.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as lithium, amiodarone (used for heart rhythm problems), or certain anti-thyroid drugs, can interfere with thyroid function and lead to hypothyroidism.
- Congenital factors: Some individuals are born with an underactive thyroid gland or have genetic abnormalities that impair thyroid hormone production.
- Hyperthyroidism Causes:
- Graves’ disease: This is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to overproduce thyroid hormones.
- Toxic adenomas or multinodular goiter: These are non-cancerous growths or nodules in the thyroid gland that produce excessive amounts of thyroid hormones.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland, whether caused by a viral or bacterial infection, can temporarily result in the release of excess thyroid hormones.
- Excessive iodine intake: In some cases, consuming too much iodine, either through diet or medications, can trigger hyperthyroidism.
- Pituitary gland malfunctions: Rarely, a tumor or abnormality in the pituitary gland (located in the brain) can lead to the overproduction of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones.
It’s worth noting that for certain thyroid conditions, the exact cause may not always be known or may involve a combination of factors. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an endocrinologist, for a thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause of a thyroid disorder.
PREVENTION OF THYROIDISM
While it may not be possible to prevent all types of thyroid disorders, there are certain measures you can take to promote thyroid health and potentially reduce the risk of developing thyroid disorders. Here are some prevention strategies:
Ensure Sufficient Iodine Intake: Iodine is a vital mineral required for the production of thyroid hormones. Include iodine-rich foods in your diet, such as iodized salt, seafood, seaweed, dairy products, and eggs. However, be cautious not to consume excessive amounts of iodine, as it can also have negative effects.
Balanced Diet: Maintain a healthy and balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. A well-nourished body supports overall thyroid function.
Limit Goitrogenic Foods: Some foods contain compounds called goitrogens that can interfere with thyroid function. While cooking or steaming these foods can minimize their impact, it’s advisable to consume them in moderation. Examples of goitrogenic foods include cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, and kale), soy-based products, millet, and certain nuts.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to thyroid dysfunction. Implement stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities you enjoy. Adequate sleep and relaxation are also important for maintaining overall health.
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise or physical activity as it promotes general well-being and helps regulate hormone levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with strength training exercises.
Regular Check-ups: Attend routine medical check-ups and discuss any concerns related to your thyroid health with your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring of thyroid function can help detect any abnormalities early on.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of thyroid disorders, particularly Graves’ disease and thyroid cancer. If you smoke, consider seeking support to quit smoking.
Be Caerful of Radiation Exposure: Limit unnecessary exposure to radiation, such as medical imaging tests, and ensure that appropriate shielding is used when undergoing radiation therapy.
DIAGNOSIS FOR THYROIDISM
The diagnosis of a thyroid disorder involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process for thyroid disorders:
-
Medical History Review: Your healthcare provider will begin by discussing your symptoms, medical history, and any family history of thyroid disorders. They will ask about specific symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, heat or cold intolerance, and any visible swelling or lumps in the neck.
-
Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted to assess the size and condition of your thyroid gland. Your healthcare provider will palpate your neck to check for any enlargement (goiter) or the presence of thyroid nodules.
-
Thyroid Function Tests: Blood tests are commonly used to evaluate thyroid function. These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. Abnormal levels of these hormones can indicate hypo- or hyperthyroidism.
-
Additional Blood Tests: In some cases, your healthcare provider may order additional blood tests to check for specific antibodies associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease.
-
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests may be used to visualize the thyroid gland and identify any structural abnormalities or nodules. Ultrasound is commonly used to assess the size, shape, and texture of the thyroid gland and to determine the presence of nodules or cysts.
-
Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If nodules are detected during the physical examination or imaging tests, your healthcare provider may recommend a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. This involves using a thin needle to extract a small sample of cells from the thyroid nodule for further analysis. The biopsy helps determine if the nodule is benign or cancerous.
-
Thyroid Scan: In certain cases, a thyroid scan may be performed to evaluate the function of the thyroid gland. This involves taking a small amount of radioactive material orally or intravenously, which is then absorbed by the thyroid gland. A special camera is used to detect the radioactive material and create images of the thyroid gland’s activity.
THYROID DISORDER MANAGEMENT BY DR MONGA MEDI CLINIC
If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or have been diagnosed with thyroid disease, we encourage you to contact Dr. Monga Medi Clinic. We invite you to schedule a consultation with our expert team at Monga Medi Clinic. We are committed to providing exceptional care, personal attention, and effective treatment options to help you regain control of your thyroid health, and live a full life. Contact us today to take the first step towards a better future.
Diagnosed by experts: Our clinic begins your journey to recovery with a thorough evaluation and diagnosis of your symptoms. Our experienced endocrinologists will review your medical history and perform tests that will accurately diagnose your thyroid condition. These tests may include blood tests to measure hormone levels, ultrasound imaging of the thyroid gland, or micro-needle aspiration to check for lumps or growths Individual
Treatment Plan: Once we determine the nature and severity of your underactive thyroid, our team will develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. We believe in having a multifaceted approach that combines medical expertise, advanced technology and patient-centered care. Depending on the severity of your condition, our treatment plans may include medications, lifestyle changes, dietary recommendations, or surgery.
Lifestyle changes: In addition to medication, we emphasize the importance of lifestyle changes to support your thyroid health. Our team will provide guidance on obtaining a balanced diet, including foods rich in iodine, selenium, and other nutrients needed for more thyroid function. We recommend stress reduction strategies, regular exercise and adequate sleep to promote overall wellness and thyroid health.
Ongoing support and follow-up: At Dr. Monga Medi Clinic, we believe in building long-term relationships with our patients. We provide ongoing support and guidance throughout your healing journey. Our team will schedule regular check-ups to monitor your progress, adjust treatment plans if necessary, and address any concerns. Your well-being is our top priority, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.
THYROIDISM MANAGEMENT THROUGH AYURVEDA
Ayurveda, a traditional system of medicine originating from India, offers holistic approaches for promoting overall health and addressing various health conditions, including thyroid disorders. It is important to note that Ayurvedic treatments should be used as complementary therapies alongside conventional medical care, and it’s crucial to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner or healthcare professional for guidance. Here are some Ayurvedic principles and treatments that are commonly used in managing thyroid disorders:
Diet and Nutrition: Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet to support thyroid health. This may involve consuming whole, unprocessed foods, including fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Certain Ayurvedic herbs and spices, such as ashwagandha, guggul, and turmeric, are believed to support thyroid function.
Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic herbs are often used in the form of herbal formulations or supplements to support thyroid health. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is commonly recommended for its adaptogenic properties, which may help balance hormone levels and reduce stress. Other herbs like guggul (Commiphora mukul) and Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) may also be used to support thyroid function.
Yoga and Meditation: Ayurveda incorporates yoga and meditation as integral components of healing and overall well-being. Certain yoga poses, such as Sarvangasana (shoulder stand) and Matsyasana (fish pose), are believed to stimulate the thyroid gland and promote its healthy functioning. Meditation and relaxation techniques can also help manage stress, which may have an impact on thyroid health.
Ayurvedic Therapies: Ayurvedic therapies like Abhyanga (warm oil massage), Shirodhara (pouring of warm oil on the forehead), and Panchakarma (detoxification therapies) are sometimes recommended to help balance the body, reduce stress, and support overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications: Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This includes following a regular daily routine, getting adequate sleep, managing stress levels, and engaging in moderate exercise or physical activity.
It is essential to remember that while Ayurveda may offer supportive measures for thyroid disorders, it is not a substitute for conventional medical treatment. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or an experienced Ayurvedic practitioner who can provide personalized advice based on your specific condition and medical history. They can help develop an integrative approach that combines Ayurvedic principles with evidence-based conventional treatments for optimal management of thyroid disorders.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It produces hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate metabolism, growth, and development throughout the body.
Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on the specific condition. Hypothyroidism is typically treated with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement medication. Hyperthyroidism may involve medications to control hormone levels, radioactive iodine therapy, or thyroid surgery. Thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer may require surgical removal or other treatments like radioactive iodine therapy or targeted therapies.
Some thyroid disorders can be managed effectively with appropriate treatment and regular monitoring, allowing individuals to lead normal lives. However, certain conditions, such as autoimmune thyroid diseases, may require lifelong management.
If you suspect a thyroid disorder or have been diagnosed with one, it is advisable to consult with an endocrinologist—a specialist who focuses on hormonal disorders, including thyroid disorders.
Thyroid disorders can impact fertility and pregnancy. It is important for individuals planning to conceive or who are pregnant to have their thyroid function monitored and managed appropriately for optimal maternal and fetal health.